IEC 60870-5-103
IEC 60870-5-103 is a protocol for power system monitoring and controlling. Mostly used for communication between protection devices and devices of a control system in a substation (RTU) over fiber optics.
Info about protocol
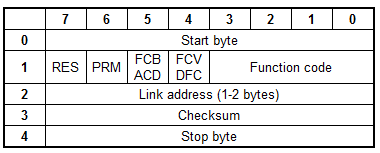
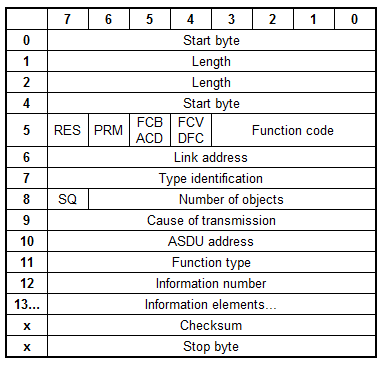
Telegram Structure
Telegram format with fixed length
Telegram format with variable length
- RES - Reserved
- PRM - 1 if master, 0 if slave
PRM = 1
- FCB - alternating bit for successive services per station
- FCV - (if FCV=1 FCB enabled)
PRM = 0
- ACD - access demand (if ACD=1 there are class 1 data)
- DFC - data flow control (if DFC=1 further messages may cause data overflow)
Function Code
PRM=1
|
Dec |
Frame type |
Service function |
FCV |
|
0 |
SEND/CONFIRM expected |
Reset of remote link |
0 |
|
1 |
SEND/CONFIRM expected |
Reset of user process |
0 |
|
2 |
SEND/CONFIRM expected |
Reserved |
- |
|
3 |
SEND/CONFIRM expected |
User data |
1 |
|
4 |
SEND/REPLY expected |
User data |
0 |
|
5 |
|
Reserved |
- |
|
6 |
|
Reserved |
- |
|
7 |
|
Reserved |
- |
|
8 |
REQUEST for access demand |
Expected response specifies access demand |
0 |
|
9 |
REQUEST/RESPOND expected |
Request status of link |
0 |
|
10 |
REQUEST/RESPOND expected |
Request user data class 1 |
1 |
|
11 |
REQUEST/RESPOND expected |
Request user data class 2 |
1 |
|
12 |
|
Reserved |
- |
|
13 |
|
Reserved |
- |
|
14 |
|
Reserved |
- |
|
15 |
|
Reserved |
- |
PRM=0
|
Dec |
Frame type |
Service function |
|
0 |
CONFIRM |
ACK: positive acknowledgment |
|
1 |
CONFIRM |
NACK: message not accepted, link busy |
|
2 |
|
Reserved |
|
3 |
|
Reserved |
|
4 |
|
Reserved |
|
5 |
|
Reserved |
|
6 |
|
Reserved |
|
7 |
|
Reserved |
|
8 |
RESPOND |
User data |
|
9 |
RESPOND |
NACK: requested data not available |
|
10 |
|
Request user data class 1 |
|
11 |
RESPOND |
Request user data class 2 |
|
12 |
|
Reserved |
|
13 |
|
Reserved |
|
14 |
|
Reserved |
|
15 |
|
Reserved |
Type identification
Standard IEC 60870-5-103 data types[1-255]
- [1-31] - standard definition
- [32-255] - for special use
|
Dec |
Description |
Direction |
Support |
|
1 |
Time-tagged message |
Monitor |
Yes |
|
2 |
Time-tagged message with relative time |
Monitor |
Yes |
|
3 |
Measurands I |
Monitor |
Yes |
|
4 |
Time-tagged measurands with relative time |
Monitor |
Yes |
|
5 |
Identification |
Monitor |
Yes |
|
6 |
Clock synchronization |
Both |
Yes |
|
7 |
General interrogation |
Control |
Yes |
|
8 |
End of general interrogation |
Monitor |
Yes |
|
9 |
Measurands II |
Monitor |
Yes |
|
10 |
Generic data |
Both |
No |
|
11 |
Generic identification |
Monitor |
No |
|
20 |
General command |
Control |
Yes |
|
21 |
Generic command |
Control |
No |
|
23 |
List of recorded disturbances |
Monitor |
No |
|
24 |
Order for disturbance data transmission |
Control |
No |
|
25 |
Acknowledgment for disturbance data transmission |
Control |
No |
|
26 |
Ready for transmission of disturbance data |
Monitor |
No |
|
27 |
Ready for transmission of a channel |
Monitor |
No |
|
28 |
Ready for transmission of tags |
Monitor |
No |
|
29 |
Transmission of tags |
Monitor |
No |
|
30 |
Transmission of disturbance values |
Monitor |
No |
|
31 |
End of transmission |
Monitor |
No |
Cause of transmission
Standard IEC 60870-5-103 cause of transmission [0-255]
- [0] - not used
- [1-63] - standard definition
- [64-255] - for special use
|
Dec |
Description |
|
1 |
Spontaneous |
|
2 |
Cyclic |
|
3 |
Reset frame count bit ( FCB ) |
|
4 |
Reset communication unit ( CU ) |
|
5 |
Start/ restart |
|
6 |
Power ON |
|
7 |
Test mode |
|
8 |
Time synchronization |
|
9 |
General interrogation |
|
10 |
End of general interrogation |
|
11 |
Return information caused by a remote command |
|
12 |
Return information caused by a local command |
|
20 |
Command "ACK positive" |
|
21 |
Command "ACK negative" |
|
31 |
Transmission disturbance data |
|
40 |
Generic write command with ACK positive |
|
41 |
Generic write command with ACK negative |
|
42 |
Generic read command data valid |
|
43 |
Generic read command data invalid |
|
44 |
Generic write conformation |
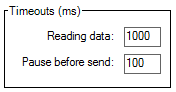
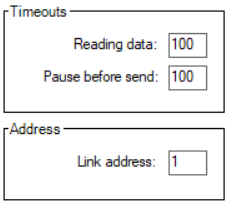
Settings
|
Timeouts (ms) |
||||
|
|
|
Monitor |
Master |
Slave |
|
Reading data |
Waiting data in serial port buffer |
Waiting data in serial port buffer |
Waiting data in serial port buffer |
|
|
Pause before send |
Not used |
Pause before send data |
Pause before send data |
|
|
Address |
||||
|
|
|
Monitor |
Master |
Slave |
|
Link |
Not used |
Remote device address |
Own system address |
|
|
ASDU |
Not used |
Remote device address |
Own system address |
|
|
Commands ack. |
||||
|
|
|
Monitor |
Master |
Slave |
|
Auto ack. system commands |
Not used |
Not used |
Auto acknowledge system commands |
|
|
Auto ack. control commands |
Not used |
Not used |
Auto acknowledge commands |
|
System
For all system functions user can set custom address:
General Interrogation
This function will send telegram Type-identification = 7
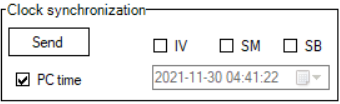
Clock synchronization
This function will send telegram Type-identification = 103 (C_CS_NA_1)
If "PC time" checkbox is checked, then the PC time will be sent. If it's not checked user can set time manually.
Time tag status bits:
- IV - invalid time
- SM - Summer/Winter
- SB - Substitute
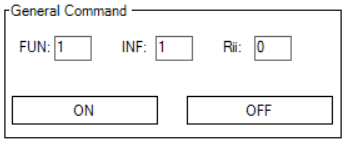
General Command
This function allows user to send command to slave device.
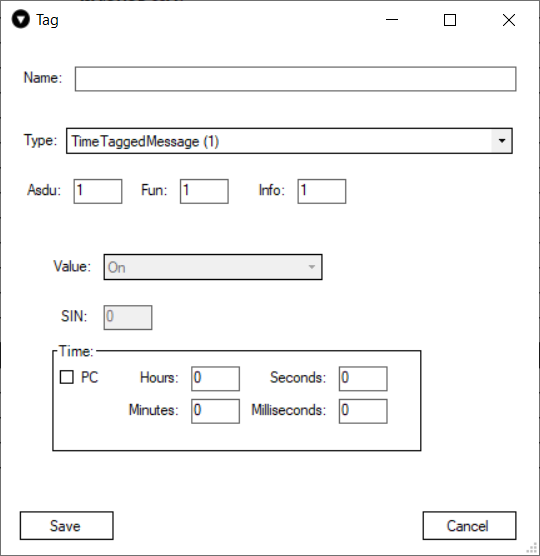
Tags
This function allows user to created named points. After points created user can send it manually or set reply checkbox to automatic reply.
There are two ways of creating tags:
Main parameters:
- Name - user-friendly tag name
- Type - the type of value.
- Asdu - Identifier of the device
- Fun - function number
- Info- Identifier of values from the device.
Here is an example image of the tag window with the TimeTaggedMessage(1) type selected. Each type has different options that can be configured when sending data. For example this type depicted in the picture below can send a value Off or On and it also is time-tagged. The user in this case can either select a specific time that they have in mind or just mark the PC checkbox and The Vinci software will automatically send the current PC time. As you can see the Value box in this example is greyed out that is because this tag is created on a master simulation, and this type doesn't support writing to slave.
Setup
To setup an IEC 60870-5-103 simulation it is fairly straightforward.
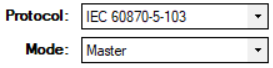
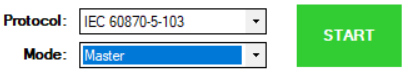
1. Select IEC 60870-5-103 and the mode.
2. Select Serial Port settings according to your device specification.
3. Select settings in the settings tab according to your device and preference.
4. Press the green START button and the simulation should start. If everything was done correctly The Vinci software should establish communication with the IEC 60870-5-103 device which you can monitor in the console tab.