# 21 Lua script runner
### Introduction
Lua is a powerful, efficient, lightweight scripting language. It has been used in many industrial applications with an emphasis on embedded systems. Lua has a deserved reputation for performance. To claim to be "as fast as Lua" is an aspiration of other scripting languages. Several benchmarks show Lua as the fastest language in the realm of interpreted scripting languages. Lua is fast not only in fine-tuned benchmark programs, but in real life too. Substantial fractions of large applications have been written in Lua.
In WCC Lite system Lua is used for extending the functionality of excel configuration adding an interface to the existing signal-linking engine. Provided functions enable to recreate PLC functionality and modify any value with ease.
### Overview
##### Execution types:
Lua runner provides 3 execution modes: interval, date, signal, which can be specified in **execution\_type**.
**Interval**: executes provided script based on provided time interval in **execution\_parameter**. It uses milliseconds, meaning if 500 value is provided, then the script is executed every 500 milliseconds.
**Date:** schedules a script execution based on provided cron expression in **execution\_parameter**. The format consists of 6-7 fields separated by space.
For example, 0 0 \* \* \* \* will execute the script at every hour mark. There are a lot of online cron expression parsers or generators to convert this expression to a more understandable sentence. [https://crontab.cronhub.io/](https://crontab.cronhub.io/)
**Signal:** uses source signal provided in signal sheet to trigger script execution. Another non excel signal can be provided in **execution\_parameter** attribute. As an example, if a signal in excel configuration has an attribute **execute** with value 1, and a source signal specified in **source\_device\_alias, source\_signal\_alias**, then if a value event happens to the source signal, the script will be executed. More than one signal can have **execute** attribute.
##### Additional functions:
To interface with existing signals and extend the available lua functions some extra functions were added:
**get, set, publish,** and **subscribe** functions are used to get the values configured in excel configuration or to communicate with other scripts.
A signal value in wcc lite system consists of 3 sub-values: **value**, **time**, and **attributes. get** function is used to get all the sub-values or **get\_value**, **get\_time** and **get\_attributes** to get only one of the sub-values. To execute this command, a signal has to be specified: **get(signal.value1).** A signal is specified by a string "tag/<device\_alias>/<signal\_alias>" or a table that is created from **iterator** parameter in excel configuration. For example:
```Lua
-- the default iterator is signals, that means there is a table 'signals' generated from excel signals
signals["tag1"] = "tag/device_alias/tag1" -- tag1 would be the signal_alias
-- to get the value of this signal:
local variable = get_value(signals.tag1)
local variable = get_value(signals["tag1"]) -- both methods are viable
-- and the 'variable' will have the value of tag1 signal
-- get function will return the value of source signal that was sent to this signal
```
Function **publish** is used to send a value to other signals:
```Lua
publish(signals.tag2, 90) -- this function will send 90 with current time to the signal tag2
publish(signals.tag2, {value = 60, time = "123456789", attributes = "iv,nt,sb"})
-- above command is used when other sub values are needed to be specified
-- and the signal-linker will send it to another signal
-- if this signal was specified as source signal in another protocol signal
```
To provide different time and attributes to the publish function, a table of these 3 values has to be specified, time can be omitted. An example of the table is returned by the **get** function.
These two functions will be used the most, others are included for communication between different scripts in a more complex system.
**set** function set the value of the signal, without sending an event of change:
```Lua
set(signal.tag3, 50) -- this command will set the value of the signal tag3
-- because it is a set function, other protocols will not see a change
-- and the value will not be accessible
-- it is only used with non excel signals
set("signal1", 60) -- now the signal1 tag will have a value
-- and another script will be able to use get to get this value
local value1 = get_value("signal1") -- value1 will be equal to 60 with current time
```
Function **subscribe** is used to wait (blocks code execution while waiting) for a value and get it. It is used the same as **get** function (does not have separate functions for sub-values). It should only be used if more complex communication between scripts is needed.
These functions are equivalent to REDIS functions.
Function **save** saves the specified value to flash memory for use after reboot. The same value sub-values apply to execution.
```Lua
save(signals.tag1, 50) -- this will save a value to tag1
-- after reboot or script runner process restart this value will be set to tag1
-- and will be accesible with get(signals.tag1)
-- this function will not set the value tag1 to 50
```
Function **time\_ms** returns current time in milliseconds and in UNIX format.
```Lua
local t = time_ms()
-- t will be equal to 1665389490555
-- if the date right now is Mon Oct 10 2022 08:11:30:555 GMT+0000
```
Function **sleep** is the same as Lua socket module function socket.sleep.
```Lua
sleep(1) -- will wait for 1 second
```
Additional functions for debug information are: **emerg, alert, crit, err, warning, notice, info, debug**. These functions correspond to levels from 0 to 7. The default level is 4, which means that the function from **emerg** to **warning** will be printed to syslog, unless specified differently in file **/etc/lua-runner.conf.**
```Lua
emerg("log message 0")
alert("log message 1")
crit("log message 2")
err("log message 3")
warning("log message 4")
notice("log message 5")
info("log message 6")
debug("log message 7")
```
These functions will require significant cpu resources even if the message log level is higher than default and no message is printed.
##### Web interface
The web interface is used to see what scripts are running, if there is a script provided, to stop/start a script. After configuring a device with lua runner as protocol, the script runner protocol hub tab will be populated with devices that where configured:
[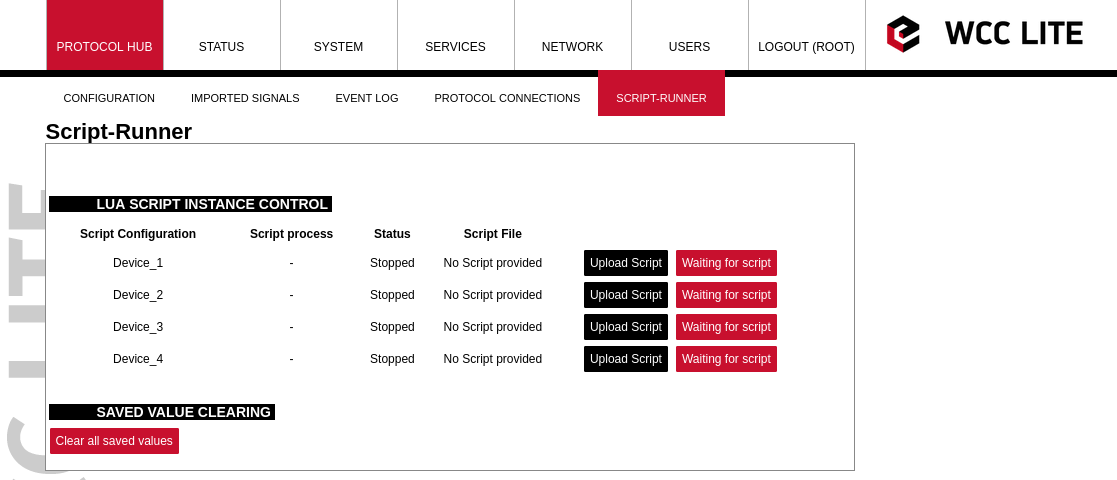](https://wiki.elseta.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/image-1665406373895.png)
Then by pressing the Upload Script button, a script will be available to be selected (the name of the script will be changed to match device\_alias). When uploaded the script will not be started automatically, pressing start will be necessary.
[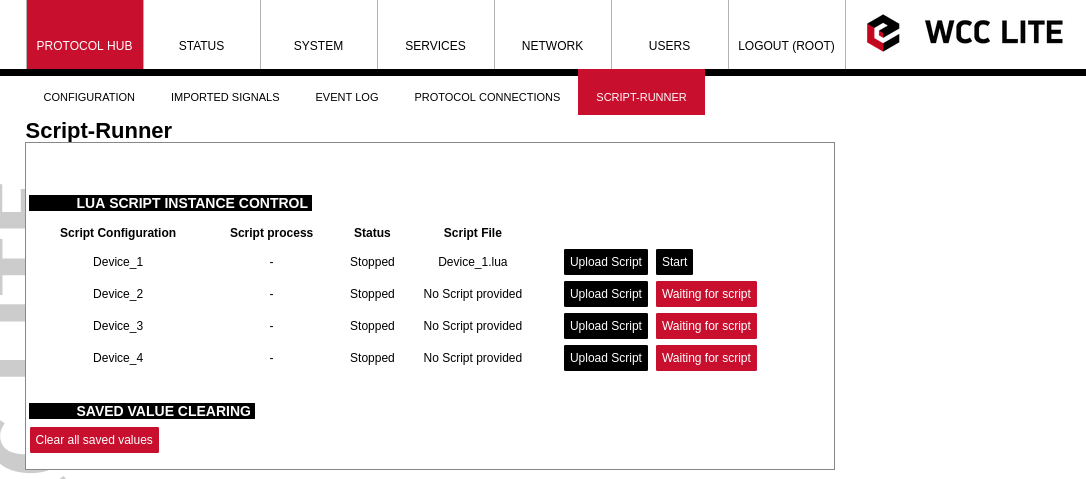](https://wiki.elseta.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/image-1665408922682.png)
After pressing start, the script will be started, if there are errors it will try to start, but after a few attempts, it will stop.
[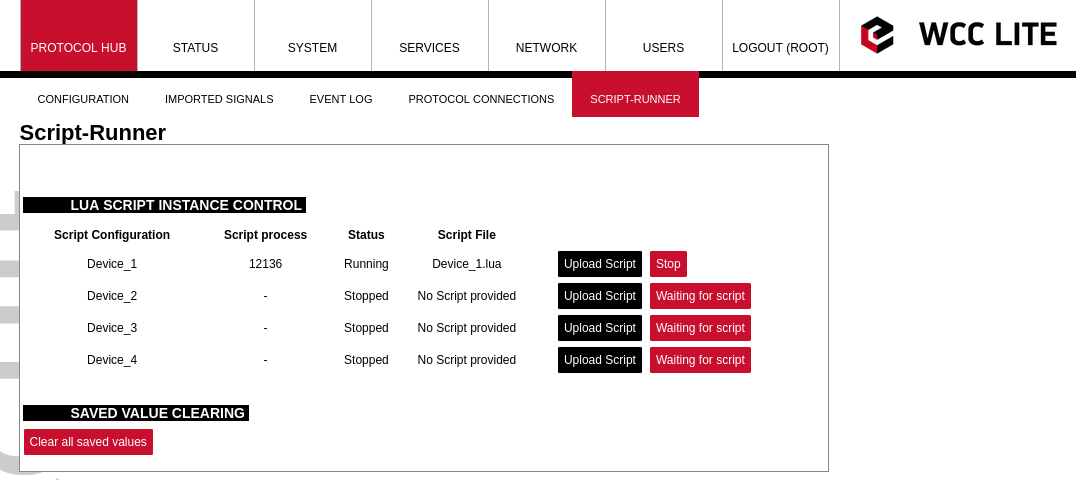](https://wiki.elseta.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/image-1665409121771.png)
Clear all saved values button is used to clear the memory of saved values. Having a lot of values being saved is not healthy for the SD card and faults can happen. Also, script runner process initialization is slowed down when a lot of saved values are used.
### Configuration
#### Device configuration parameters:
| **Parameter**
| **Type**
| **Description**
| **Required
| **Default value**
(when not specified)
| **Range**
|
| Min
| Max
|
| name
| string | User-friendly name for a device
| Yes |
|
|
|
| device\_alias
| string
| Alphanumeric string to identify a device
| Yes
|
|
|
|
| description | string | Description of a device
| No |
|
|
|
| enable
| boolean
| Enabling/disabling of a device
| No
| 1
| 0
| 1
|
| protocol
| string
| Protocol to be used
| Yes
| | lua runner
|
| execution\_type
| string
| Execution type to be used
| Yes
| | interval, date, signal
|
| execution\_parameter
| int, string
| Parameters for execution
| Yes
| | interval time in ms,
date in cron format,
additional signal
|
| queue\_max
| int
| Maximum execution queue jobs
| No
| 3
| 0 to disable queue
|
| error\_limit
| int
| Error limit before stoping
| No
| 3
| 0 to disable
|
| keep\_alive\_time\_ms
| int
| Time to keep the script alive in ms
| No
| 600000
| 0 to disable
|
#### Signals configuration parameters:
| **Parameter**
| **Type**
| **Description**
| **Required
| **Default value**
(when not specified)
| **Range**
|
| Min
| Max
|
| signal\_name
| string | User-friendly name for a signal
| Yes |
|
|
|
| device\_alias
| string
| Alphanumeric string to identify a device
| Yes
|
| Must match device\_alias in the device sheet
|
| signal\_alias
| string
| Unique alphanumeric name of the signal to be Yes used
| Yes
|
|
|
|
| iterator
| string
| Lua table name to which signal is added
| No
| signals
| | |
| default\_value
| string
| Default value for a signal
| No
| | | |
| execute
| int
| Enable signal update trigger to execute script (only available for signal execution mode)
| No
| 0
| 0
| 1
|
Math (math\_expression, add, multiply, ) for source signals will not work for lua-runner device
### Debugging the script runner service
If configuration for script runner is set up, the process will start automatically. If configuration/script is missing or contains errors, process will not start. It is done intentionally decrease unnecessary memory usage.
Script runner runs a service called **lua-runner**. If the script doesn't start or does not work correctly, a user can launch a debug session from command line interface and find out what problem is causing it to not work. To launch a debugging session, a user should stop the script from web interface and run **lua-runner** command with respective flags and configuration as in the table given below.
Procedure for lua-runner service debugging:
- **Step 1**: Script must be stopped through web interface.
- **Step 2**: After script is stopped it must be started with the preferred configuration file (JSON files found in /etc/lua-runner, and the name corresponds to device\_alias) and a debug level 7: **lua-runner -c /etc/lua-runner/device\_alias.json -d7 -e.**
- **Step 3**: Once the problem is diagnosed normal operations can be resumed by starting the script through web interface.